Projects
Characterization of heteroaggregates of alginate microparticles and chitosan nanoparticles using fluoroscence spectroscopy (MS thesis, Advisor: Dr. Nina Shapley)
I worked on developing fluorescence spectroscopy as novel method to characterize heteroaggregates of alginate microparticles and chitosan nanoparticles. These heteroaggregates, where surface of each freely suspended microparticle is coated with nanoparticles have wide range of application such as water purification, drug delivery system, flocculating agents etc.
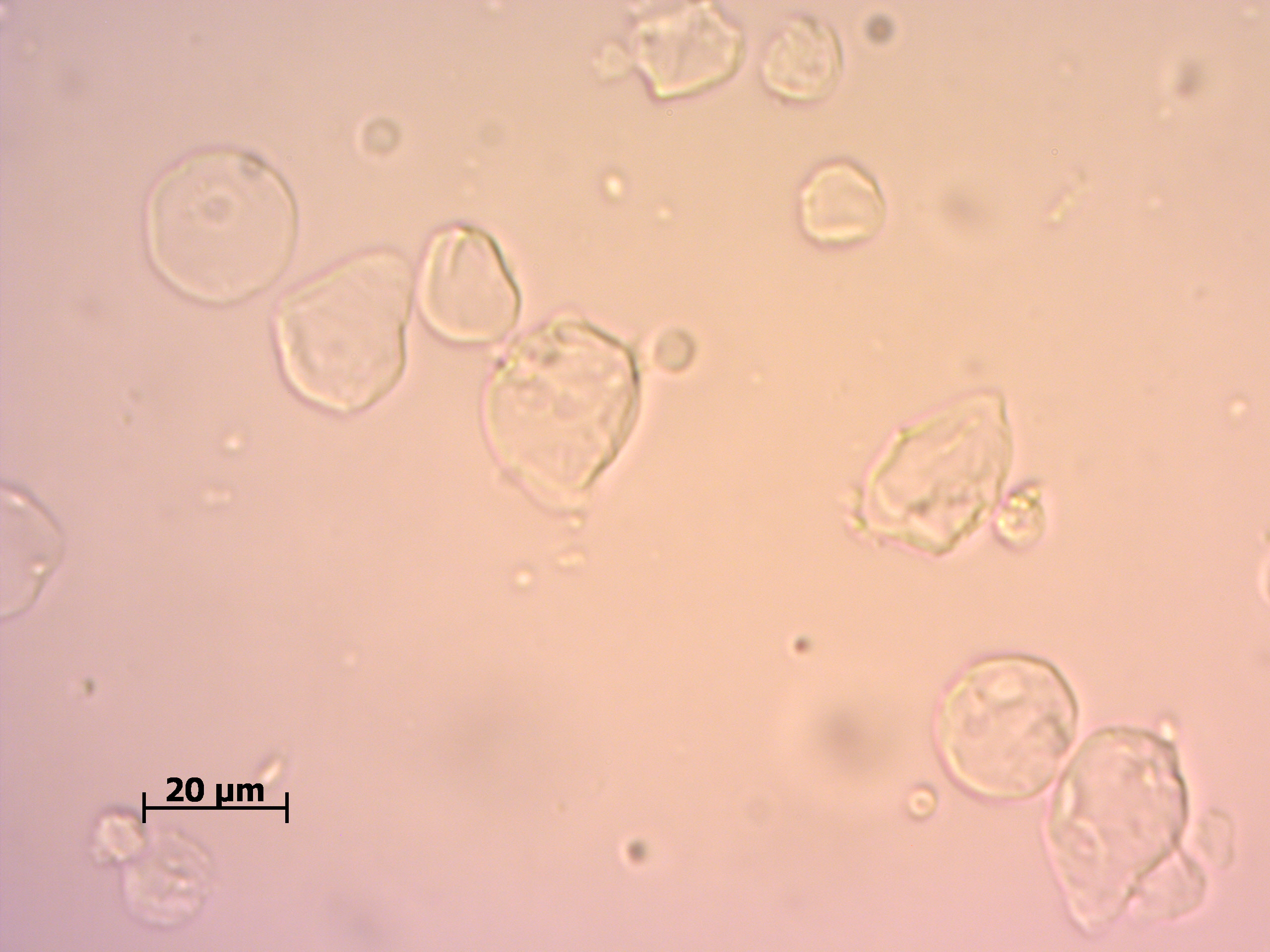
When oppositely charged microparticles and nanoparticles are mixed together, aggregation tends to occur. The specific type of interaction and resulting aggregate morphology that occurs is dependent on particle concentration. The different types of interactions can be distinguished at boundaries according to concentration ratios. Unfortunately, particle interaction regime boundaries can only be determined visually by using microscopy or by using not typically available techniques such as ultra-small-angle X-ray scattering. We are developing fluorescence spectroscopy as novel method to distinguish between dispersed vs. agglomerated morphologies using a fluorophore that would give different intensity output in each of the interaction regime. If successful, it can be of great advantage as to identify aggregates in situ using fluorescence spectroscopy. I studied different factors such as concentration ratio of alginate and chitosan particles, pH, salt concentration etc. and their effect on interaction regime boundaries of alginate-chitosan hetero-aggregates. My particular interest being acidic pH environment and its effect on hetero-aggregates with possible application in drug delivery system. Using laser diffraction scattering, I obtained particle size distribution of these aggregates to help understand size dependence on concentration ratio.
Axial dispersion in rotating cylinders for dilute systems (Engineering Research Center for Structured organic Particulate Systems, ERC-SOPS)
I was part of the group which studied axial dispersion in rotating cylinders. Much of previous works have focused on free flowing materials but not as much on cohesive materials. We investigated how fast mixing occurs for single as well as binary systems using different excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredients. Since product performance greatly depends on blend homogeneity, consequences of variability can be severe. This project will give us better insight into how mixing is affected by different factors and tools to have better control over the process. We etablished relation between flowability and bed behaviour (cascading, cataracting, centrifuging) for acetaminophen, lactose monohydrate and MCC. We also determined axial dispersion coefficient from concentration vs axial position profiles measured for series of time points. We presented our findings at recent AICHE conference.

Determination of size and charge density of surfactant micelles
This goup project involved studying effect of surfactant addition on size distribution and zeta potential of zein protein particles in aqueous solution. We used 6 different surfactants. The main difficulty was to prepare zein solution as zein has very low solubility in water. We solved that problem by using ethanol-water mixture to dissolve zein and then evaporating ethanol to get suspended zein particles. We were able to identify best surfactant which gave higher zeta potential and reduced particle size.
Development and Characterization of Novel Insulation Material Using Industrial Waste (Final year project, Advisor: Dr. Sachin Mandavgane)
The project was sponsored by DST (Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India), to find ways of using the sludge from recycled-paper mills as for insulation and thus conserve heat energy and take care of waste disposal as well. To find thermal conductivity of samples of waste and to assess their efficiency as insulating material, I subjected the samples to XRD, XRF, Ultimate Analysis and Proximate Analysis. TGA-DSC analysis revealed various thermal properties for the samples. We decided to obtain thermal conductivity versus composition and relative humidity data. We used Lee’s disc method to measure the conductivity of samples containing different proportions of cement and moisture levels and tested their thermal insulation characteristic on a piping system. We applied 5 mm thick layers of samples of sludge and cement mix to the pipes carrying hot water and used 4-probe thermometer system to take the readings for inflowing and out-flowing hot water and at two intermediate points. We also tested the mixtures on vessels containing hot water. Temperature variation between insulated and bare portions of the pipes and vessels were compared by Thermal imaging. For further experiments we replaced water with gear-oil and lube-oil. We developed cheap and effective insulating material.